What CPU is Compatible with my Motherboard
“what CPU is compatible with my motherboard” can be a frequently asked question if you’re upgrading your CPU or starting from fresh.
When installing a computer, compatibility with the motherboard and CPU is critical. However, you can check out our article on how to remove CPU cooler if you are facing compatibility issues
So, in this post, you will learn how to verify if that specific processor chip, whether Intel or AMD, is compatible or not with your Motherboard’s CPU socket, as well as how to make sure everything works. As a result, you will be able to determine which processors are compatible with your Motherboard, and you will be able to install the most reliable and powerful CPU available at the time. You will prevent incompatibility issues and many errors this way.
CPU and motherboard compatibility
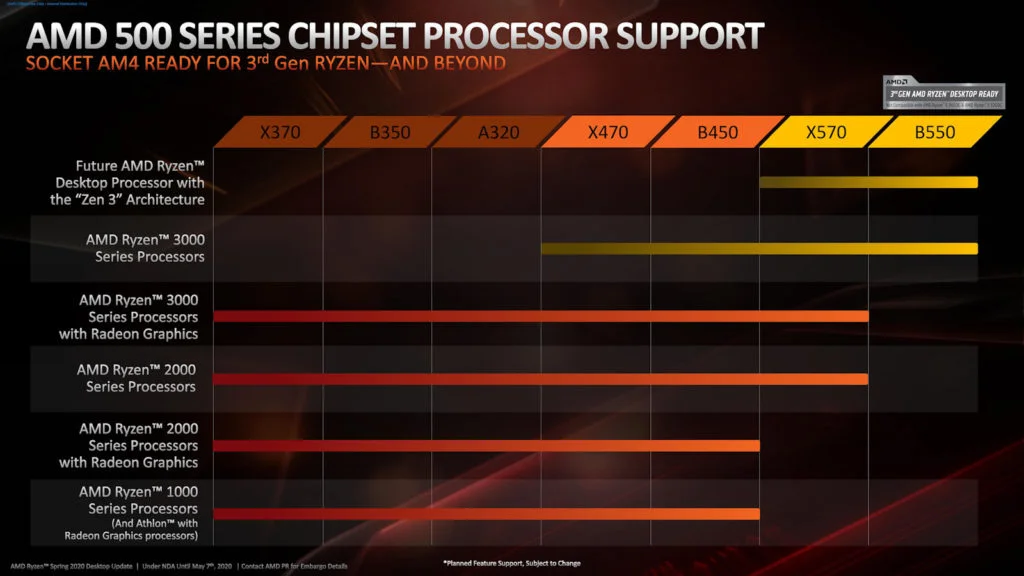
Each CPU has a unique socket need, which may be found in their specs.
The LGA1200 socket, for example, is required by the newest Intel 10th and 11th Gen desktop CPUs, but the AMD Ryzen 1000, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 series desktop processors require the AM4 socket. When you search up the motherboard specifications online, you’ll see that they don’t mention all of the CPU models that are supported.
Hence If you won’t find out what CPU cooler you have, you can check our related article. They will instead merely state the CPU socket they have. You may use this socket information to figure out which CPU models the motherboard will support. The motherboard’s socket has a lot to do with the chipset it uses. The chipset is responsible for a number of aspects of the motherboard, including the socket.
When it comes to CPU compatibility, there are three things to consider: the CPU socket, the motherboard chipset, and BIOS compatibility.
Also read: your CPU fan might become blocked with dirt if you aren’t attentive, disrupting your entire operation and giving you a lot of hassle and unexpected charges. Hence it is important to learn how to clean CPU cooler.
CPU socket
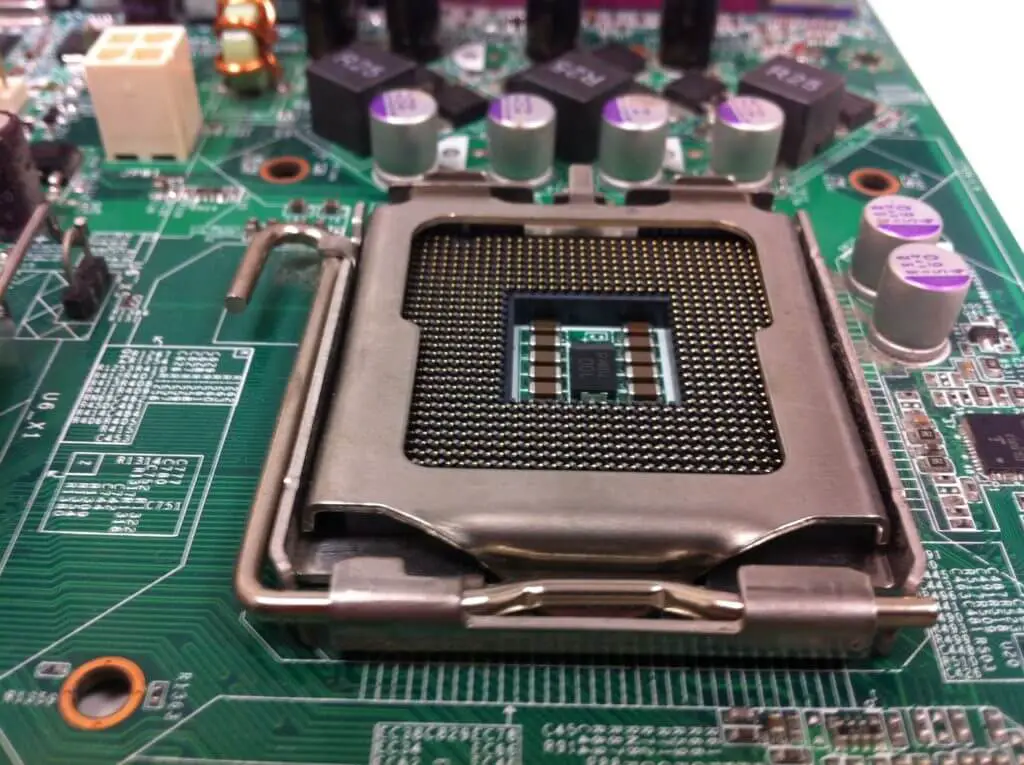
For starters, determine the sort of CPU socket your motherboard has. The CPU socket is the motherboard connection where your CPU is plugged in. Specific types of sockets are included in the motherboard’s specs for each motherboard series. To enable CPU interaction with your motherboard, each CPU socket has its physical properties and pin configuration. Because AMD and Intel CPUs use distinct sockets, you’ll need an AMD-compatible motherboard for an AMD processor and an Intel-compatible motherboard for an Intel processor. There’s no getting around it. The following are examples of common Intel CPU sockets:
- LGA 1151
- LGA 1150
- LGA 1200
- LGA 1700.
AM4 is the CPU socket used by AMD Ryzen 1000, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 series processors. TR4, sTRX4 (for AMD Threadripper CPUs), and LGA2066, LGA4189 (for Intel X-Series CPUs and select Xeons) are among few of the best Desktop and Server Sockets. Since every motherboard is manufactured with a certain kind of socket, it is important that you know how to figure out which one it has in order to ensure compatibility. Your CPU will not be able to physically plug into your motherboard if it has a socket that is incompatible with it.
LGA, PGA, and BGA are the three types of CPU surface mounting mechanisms used on motherboards.
Motherboard chipset
You won’t have to worry about chipsets if you follow your motherboard’s specs and the CPU Support List that can be found online for any motherboard. You can only trust the manufacturer’s testing and updating of the CPU support list. It’s the only certain way to figure out which CPUs will work with your particular motherboard.
BIOS compatibility
Another important aspect to look for when buying a new CPU is BIOS compatibility. A column will indicate ‘Validated BIOS’ or ‘Validated since BIOS’ or anything similar from the same CPU support list you discovered before. This indicates that the CPU in that list will work with the motherboard, but only if you have the BIOS Version shown in that row, at the very least.
Once you’ve figured out which motherboard you have, just Google and search the brand and type of your motherboard, accompanied by the words “specs” or “specifications.”
The very first link will direct you to a page on the authorized manufacturer’s website that neatly lists all of the specifications for your motherboard. The quickest method to determine your BIOS version is to put ‘Command Prompt’ into the ‘Windows’ search box.
Open the Command Prompt and enter: wmic bios get smbiosbiosversion.
The version of your BIOS that is currently installed will be shown.
You now can verify your current BIOS version to the lowest BIOS version required by your new CPU. If you’re current BIOS has to be upgraded, go return to the company’s website and find your motherboard model. Once it comes to setting the BIOS, each manufacturer has its own set of instructions.
It usually entails saving the updated BIOS version to a USB device and then starting your machine from it. Other manufacturers provide you the option to upgrade the BIOS from the BIOS starting menu. Keep in mind that you should only upgrade your BIOS if your new CPU demands it. It will not be able to run if you do not update your BIOS before installing the new CPU.
What motherboard do I have?
To figure out which CPUs are compatible with your motherboard, you’ll need to look up the brand and model.
There are a few options for accomplishing this.
- The first method is to locate the box in which your motherboard was sent.
- If you purchased the motherboard online, check the confirmation email to see if the name of your motherboard is mentioned.
- You may also use the System Information utility on your PC.
- Another approach is to use a free tool called CPU-Z to locate your motherboard if you’re having difficulties finding it. This software collects and shows the information on your computer’s key components.
Asus motherboard CPU compatibility
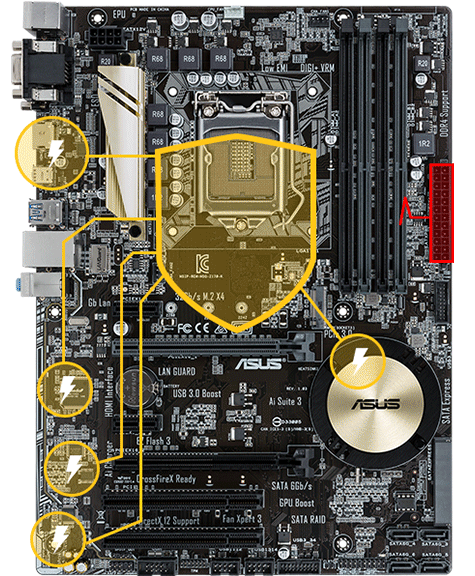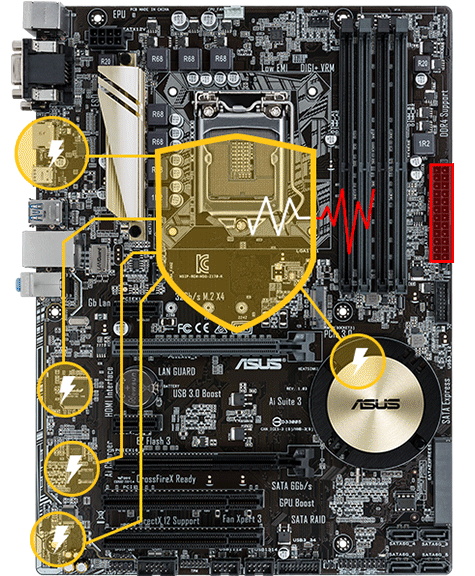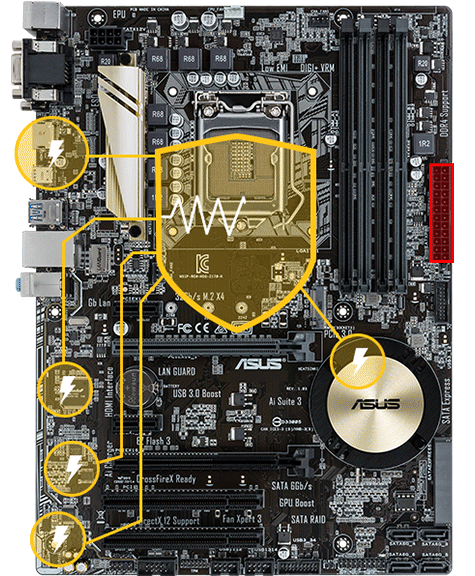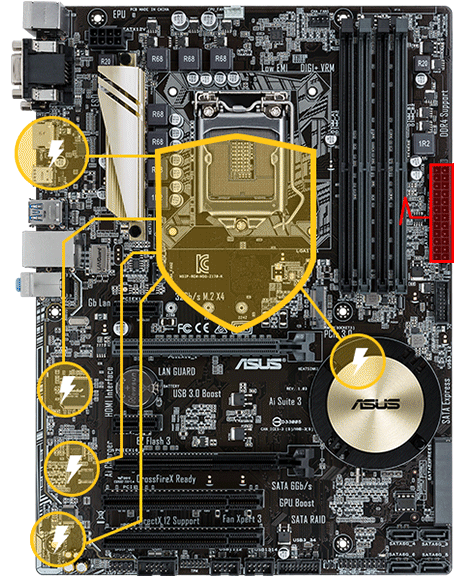
TUF devices have long been positioned by Asus as dependable solutions with reasonable cost and a more basic feature set. As a result, this is a wonderful low-cost solution for someone looking for a simple, strong, and dependable system.
Given the high cost of many Z590 motherboards, this is a nice improvement. asus z97-a compatible cpu is one of its main features. The ASUS Z97-A ATX Motherboard offers an LGA1150 socket that takes 4th and 5th generation Intel CPUs and supports up to 32GB of DDR3 RAM modules, allowing you to combine and optimize all of your computer components.
lga 1150 compatibility
Haswell (fourth-generation Intel Core) CPUs are supported by the LGA 1150 socket. This socket also works with the few fifth-generation Core desktop CPUs that have been released. It may be found on six distinct chipsets, including the H81, B85, Q85, Q87, H87, and Z87, as well as additional Intel sockets.
The Intel C222, C224, and C226 chipsets are used by Intel Xeon processors for socket LGA 1150.
LGA 1150, often known as Socket H3, is a microprocessor socket utilized by Intel’s Haswell microarchitecture central processing units (CPUs). This socket is also utilized by the Broadwell microarchitecture, which is Haswell’s successor.
Conclusion: What CPU is compatible with my motherboard:
What CPU is compatible with my motherboard is to determine what socket it supports and then select a motherboard that supports that socket. Sockets are also common throughout multiple versions of motherboard chipsets. If you want to use a CPU from the newest generation, we recommend obtaining the latest motherboard chipset series.
The computer will not operate if the CPU fits all of the pins on the motherboard yet there is no compatibility between them. The only thing you’ll see is a dark screen. There should be no harm to the CPU’s electronic components. You will, however, need to perform a BIOS update if the two computers are running different versions of the operating system.
The BIOS upgrade will make the PC run faster. If you crammed the processor into the CPU socket, it’s obvious that they’re not compatible. The motherboard and CPU will be harmed as a result of this.
Check the CPU model number, stepping code, and motherboard serial number to see if your CPU is compatible with your motherboard. For the computer to work effectively, the motherboard, CPU, GPU, RAM, hard drives, cooling fans, power supply, monitor, and even the casing or chassis must all be compatible.
Any discrepancy will either cause the computer to stop working or cause harm to its components. Hence it’s important that everything is connected and compatible to avoid any short-circuits and failure, even if they don’t affect the PC immediately, long-term effects can be bad.